Taking a B-complex vitamin can help your health if you cannot get enough B vitamins from the rest of your diet. People who are pregnant, vegans, or have specific medical conditions fall into this category.
There are eight different types of B vitamins and they can be found in a wide variety of foods. As a result, most people consume the required daily amounts of these vitamins simply by consuming their regular diet.
However, there are several factors that could potentially cause your body to require additional amounts of B vitamins. These include:
Age
Pregnancy
Dietary Choices
Age
Pregnancy
Dietary Choices
Genetic Factors
Medication Use
Alcohol Consumption
If one of these factors applies to you, then taking a B-complex vitamin may be advisable. B-complex vitamins typically refer to supplements that contain all eight B vitamins.
Below are the potential health benefits associated with B-complex vitamins, as well as the suggested dosages and possible side effects.
What are B-complex Vitamins?
B-complex supplements generally consist of all eight B vitamins in a single tablet.
B vitamins are water soluble, therefore your body will eliminate excess B vitamins through urine. Therefore, you must consume B vitamins every day in the form of food.
Each B vitamin has multiple beneficial functions and are required to maintain optimal health.
The following are the typical B vitamins found in B-complex supplements:
B1 (Thiamine)
Thiamine serves a critical role in metabolism; it assists in converting the nutrients we consume into usable energy. The richest food sources of thiamine include sunflower seeds, and wheat germ.
B2 (Riboflavin)
Riboflavin helps to convert food into energy and works as an antioxidant. Organ meats, beef, and mushrooms are high in riboflavin.
B3 (Niacin)
Niacin is essential for cellular communication, metabolism, and DNA repair. Chicken, tuna, and lentils are rich in niacin.
B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Like the other B vitamins, pantothenic acid enables the body to derive energy from the food we eat and aids in the production of hormones and cholesterol. Rich sources of pantothenic acid include liver, fish, yogurt, and avocado.
B6 (Pyridoxine)
Pyridoxine is responsible for the metabolism of amino acids, the production of red blood cells, and the synthesis of neurotransmitters. Chickpeas, salmon, and potatoes are high in pyridoxine.
B7 (Biotin)
Biotin is required for the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats and to regulate gene expression. Good sources of biotin include yeast, eggs, salmon, cheese, and liver.
B9 (Folate)
Folate facilitates the production of new cells and the metabolism of amino acids and is essential for the production of red and white blood cells and for the proper division of cells. Leafy greens, liver, and beans are the richest food sources of folate. Supplements containing folic acid provide another source of folate.
B12 (Cobalamin)
Perhaps the most well recognized of the B vitamins, B12 is crucial for neurological function and DNA production as well as for the maturation of red blood cells. B12 is found primarily in animal-based products such as meat, eggs, seafood, and dairy.
While each of the B vitamins shares similarities, they each serve unique functions and are required in varying amounts.
Who Should Take Vitamin B Complex?
Because B vitamins are present in so many foods, you are unlikely to experience a deficiency unless you consume a poorly balanced diet.
However, various factors can increase your need for B vitamins, thereby necessitating supplementation.
Pregnant and Nursing Individuals:
During pregnancy, the requirement for B vitamins increases, particularly B12 and folate, due to their necessity for supporting the development of the fetus.
Individuals who are either pregnant or breastfeeding, especially those who consume a vegetarian or vegan diet ,will find it essential to supplement their diet with a B-complex vitamin.
A deficiency in B12 or folate during pregnancy or lactation can result in severe neurologic impairment to the fetus or newborn.
Older Adults:
With aging comes the inability to effectively absorb vitamin B12 and a decrease in appetite, which makes it challenging for some individuals to consume sufficient amounts of B12 through diet alone.
Effective absorption of B12 from dietary sources depends upon the presence of adequate stomach acid.
However, it is believed that many older adults do not produce sufficient stomach acid to enable effective absorption of B12. In addition, if you are taking medication to reduce stomach acid to alleviate symptoms of acid reflux or heartburn, you may also be inhibiting your B12 absorption.
Individuals With Certain Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions increase an individual’s likelihood of experiencing a nutrient deficiency in B vitamins.
Examples of such conditions include:
celiac disease
Crohn’s disease
Alcoholism
Hypothyroidism
Anorexia
Additionally, individuals who have undergone certain forms of weight loss surgery are also more likely to be deficient in B vitamins.
In such cases, the advice to supplement with a B-complex vitamin is common to correct or prevent deficiencies.
Vegetarians and Vegans:
Vegetarians and vegans may be at risk of developing a B-12 deficiency because B-12 is found primarily in animal products such as; meat, dairy, eggs and fish.
In order to obtain adequate amounts of B-12 in the absence of obtaining through animal products, many vegans and vegetarians rely on fortified foods or supplements.
Taking a daily B-complex vitamin ensures that individuals who choose to adhere to a diet that eliminates animal products receive all of the essential B vitamins that they require.
Individuals Taking Certain Medications:
Certain prescription medications can cause B-vitamins deficiencies in individuals taking them.
Examples of such medications include Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI’s), which are prescription medications that lower the acid levels in the stomach, and Metformin, which is a commonly prescribed medication for diabetes, and can deplete B-12 and Folate.
Benefits of B-Vitamins:
Although there are certain medical conditions where it may be required to take B-complex vitamin supplements, research indicates that taking a B-complex vitamin supplement may be beneficial to individuals without increased nutritional requirements.
Mood Improvement and Reduced Stress:
B-complex vitamins are often utilized to reduce fatigue and improve mood. Research indicates that B vitamins can provide improved mood and enhanced cognitive function.
One study conducted on healthy adults demonstrated that supplementation with a multivitamin that contained high levels of B-complex vitamins for ninety days resulted in a reduction of negative mood symptoms.
Anxiety/Depression Symptoms Relief:
While B-complex vitamin supplements do not treat mental health disorders, B-complex vitamin supplements may help to alleviate symptoms associated with depression and/or anxiety.
A 2019 systematic review indicated that B vitamins support mood and overall brain health.
Research has established low blood levels of certain B vitamins (B12, B6 & Folate) are directly related to an increased risk of depression. Therefore, it is essential to rule out nutritional deficiencies when experiencing symptoms of depression.
Recommended Dosage:
The Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) of B vitamins differs between men and women, depending upon age, biological sex and/or pregnancy status.
For Women and Men, the RDI of B vitamins is as follows:
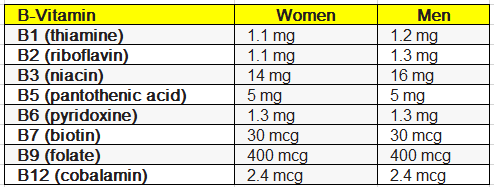
If you are experiencing a B vitamin deficiency, you may require supplementing with larger doses than those listed above to correct the deficiency.
It is therefore very important to select a B-complex supplement that is tailored to meet your individual needs for each of the B vitamins.
You may want to consult with a healthcare professional regarding your unique nutritional requirements based on your age and health status.
Possible Side Effects:
Because B vitamins are water soluble, it is highly improbable to exceed safe levels of consumption through food or B-complex supplements taken as directed.
However, consuming excessive and/or unnecessary amounts of B vitamins through supplements may result in serious adverse reactions.
Consumption of high amounts of B3 (Niacin) via supplements may result in nausea/vomiting, elevated blood sugar, skin flushing, and/or liver damage.
Additionally, high doses of B6 may result in peripheral neuropathy, photophobia, and painful skin lesions.
An additional side effect of B-complex supplements is urine that becomes bright yellow due to your body eliminating the extra vitamins that your body cannot utilize.
Always choose reputable brands of B-complex supplements that voluntarily allow their product to be independently evaluated by third party testing laboratories such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP).
Conclusion:
There is evidence to support that pregnant individuals, elderly adults, vegans and individuals with specific medical conditions may benefit from taking a B-complex supplement.
Supplementing with B-complex vitamins may also improve mood and relieve symptoms of depression.
Side effects from B-complex supplements are extremely rare, provided that you follow the recommended dosages, which vary based on; age, nutritional requirements, sex, and health status.
If you are unsure whether taking a B-complex supplement would positively impact your health, consider consulting with a healthcare professional to assist you in determining if taking a B-complex supplement is right for you.